Hi all,
This is a Basic overview of IBM Content Manager and it's components.
Content Manager provides a scalable, enterprise-wide repository system for the capture, creation, organization, management, workflow routing, archiving, and life cycle management of business content. It handles sharing, reuse, and archiving of all types of digitized content. The digitized content supported by Content Manager includes HTML and XML-based Web content, images, electronic office documents, and rich media, such as digital audio and video. Content Manager uses a triangular architecture
Architecture
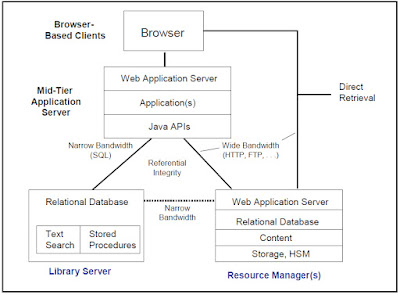
Content Manager is built on multi-tier distributed architecture, with a Library Server that manages, indexes, and searches documents, Resource Managers that manage the actual digitized objects, a mid-tier server that acts as a broker between the client and the Library Server, and Windows-based and browser-based clients that provide the graphical end-user interface to the servers. Client applications use a single object-oriented application programming interface (API) to invoke all Content Manager services, which are divided between the Library Server and one or more Resource Managers. A single implementation supports a single Library Server, along with multiple Resource Managers and clients. Multiple, distinct applications of Content Manager can be installed on a single physical server. Following fig. Shows logical model of Content Manager
Fig: Logical Model of Content Manager
1.Library Server
The Library Server manages the content metadata and is responsible for access control to all content. It maintains the indexing information for all multimedia content held in a Resource Manager. Users submit requests through the Library Server. The Library Server validates the access rights of the requesting client and then authorizes the client to directly access the object in the designated Resource Manager. The Library Server also maintains referential integrity between the indexing information and the objects themselves. The Library Server is built on IBM DB2 relational database management system (RDBMS) or Oracle. All access to the Library Server is via the database query language SQL, and all Library Server logic runs within DB2. With Content Manager, no persistent processes operate on the Library Server; all content management functions are stored procedures executed by DB2. Content metadata in the Library Server is backed up and recovered using standard database tools.
2.Resource Managers
Resource Managers are the repositories that contain the digitized content and manage the storage and retrieval of objects. The Resource Manager supports caching, replication and provides hierarchical storage management when used in conjunction with IBM Tivoli Storage Manager. A single Resource Manager can manage multiple VideoCharger systems as well. The Resource Manager architecture provides an extensible model that enables the support of additional Resource Managers in the future.
3.Mid-tier server
The mid-tier server functions as a broker that mediates communications between the client and the Library Server. It manages connections to the Library Server and, optionally, to the Resource Managers.
4.Clients
Users can access Content Manager repositories through Windows clients (thick client) or an eClient (thin client). The eClient Web application consists of JavaServer Pages (JSP), servlets, and a viewer applet that runs on IBM WebSphere Application Server. The eClient can communicate directly with the Resource Manager using Internet protocols. It can talk directly to the application server (for example, WebSphere). The eClient provides federated access to and searches across all Content Manager and non-IBM repositories
“Effort only fully releases its reward after a person refuses to quit.”
Regards,
Akhilesh B. Humbe


No comments:
Post a Comment